Late ripe cabbage varieties are appreciated because of their good keeping quality and the safety of their taste. Also their advantage is resistance to sudden changes in air humidity and diseases. Among the popular hybrids of this variety of white cabbage, gardeners are in demand by Valentine F1, whose heads weigh more than 4 kg and do not crack when ripe. Learn about the features of growing varieties further from the article.
Description and characteristic
Valentina was bred by breeders of the Moscow breeding station named after Nikolai Timofeev, the market leader in the production of vegetable crops in the CIS countries. In 2004, the hybrid was included in the State Register of the Russian Federation.
The variety is resistant to fusarium and putrefactive infections, is characterized by high fruiting and crop safety. It was zoned for cultivation in the central regions of Russia, western and eastern regions of Siberia, as well as in the Caucasus.
The hybrid crop ripens 180 days after sowing. Under favorable growing conditions, about 100 tons of cabbage can be harvested from each hectare. The average weight of the heads ranges from 4 kg. They are characterized by increased elasticity and density of gray-green foliage. Despite the dull wax coating on the surface, the head is light inside. It is located on a short stump. The variety can be stored for more than six months, because of which, in the vast majority of cases, it is used for fresh consumption. The product tastes sweet and juicy.Did you know? The ancient Romans associated the appearance of cabbage with the god Jupiter. According to legend, the fruits were formed from drops of sweat falling from the divine forehead on the ground.
Photo gallery
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Among the advantages of Valentine's cabbage, experienced gardeners note:
- high productivity;
- resistance to common diseases (fusarium, necrosis, gray rot);
- density and elasticity of the head, which allows it to be stored until June next year;
- high taste and marketability of the fruit;
- ease of transportation due to the low weight of the heads;
- resistance of fruits to cracking.
- The disadvantages of the variety can be considered:
- a short leg, because of which there is a need to spud seedlings;
- poor germination of grains.
Did you know? In ancient Rome, cabbage was revered as a festive dish and served exclusively in boiled form. And in China, these fruits were regarded as cheap food. She was steeped in wine and given to the slaves who built the Great Wall of China.
The rules for growing varieties
The hybrid ripens no earlier than six months from the time of sowing, so sowing it in open ground is pointless. Valentine is cultivated in a seedling manner. Sowing dates depend on the climatic characteristics of a particular region. For example, in temperate latitudes, this work is best planned for the second decade of April. The main thing is that by the time of transplanting the seedlings are 30–33 days old.
Sowing dates depend on the climatic characteristics of a particular region. For example, in temperate latitudes, this work is best planned for the second decade of April. The main thing is that by the time of transplanting the seedlings are 30–33 days old.
Seed preparation
Given the complaints of gardeners about the poor germination of cabbage seeds of this variety, planting material is recommended to be pre-treated with any growth stimulant (Kornevin, Ekosil, Ecogel, Zircon, Epin-Extra). For this, the grains are initially disinfected with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and after that they are dipped for several hours in the prepared solution. It is advisable to use melt or rain water warmed to room temperature.
Growing seedlings
For cabbage, fertile chernozem soil with neutral acidity or purchased for vegetable crops is preferred. Before sowing, it is important to disinfect the substrate, scalding it with boiling water or holding it for about half an hour in a preheated oven. The latter method is more risky, because excessively high temperatures over time can destroy all nutrients in the soil. The ideal containers for growing seedlings are peat pots or tablets, as well as cassettes. Their advantages are improved root aeration, environmental friendliness and nutritional value of the material, as well as a high percentage of seedling survival during transplantation. The disadvantage is the excessive sensitivity of the peat product to moisture - if you overfill the crops, the walls of the tank will be covered with mold and infect the soil. The drying up of an earthen coma is also unacceptable, otherwise it will be petrified. In the absence of such a container, you can do with ordinary wooden crates or improvised vessels. Each sprout needs a space within 5 cm.
The ideal containers for growing seedlings are peat pots or tablets, as well as cassettes. Their advantages are improved root aeration, environmental friendliness and nutritional value of the material, as well as a high percentage of seedling survival during transplantation. The disadvantage is the excessive sensitivity of the peat product to moisture - if you overfill the crops, the walls of the tank will be covered with mold and infect the soil. The drying up of an earthen coma is also unacceptable, otherwise it will be petrified. In the absence of such a container, you can do with ordinary wooden crates or improvised vessels. Each sprout needs a space within 5 cm.
Valentina is not demanding, her cultivation is not much different from the traditional way. The main conditions for the full growth of cabbage seedlings are:Important! Cabbage contains several times more nitrates than watermelon. The most harmful part of the head is the head of cabbage.
- shine;
- moderate moisture;
- cool (within + 12 ... + 18 ° C).
 Emerging seedlings should be moistened to the extent necessary. The hybrid does not require top dressing, diving, and pinching. A week before the transplant, the seedlings are hardened, gradually accustoming to changing the microclimate. To this end, plants are exposed to fresh air after a peak in solar activity. Initially, air baths last 10-15 minutes, but gradually this period increases to 7-8 hours. It is strongly not recommended to leave the seedlings of cabbage open at night, because in the spring frosts are possible.
Emerging seedlings should be moistened to the extent necessary. The hybrid does not require top dressing, diving, and pinching. A week before the transplant, the seedlings are hardened, gradually accustoming to changing the microclimate. To this end, plants are exposed to fresh air after a peak in solar activity. Initially, air baths last 10-15 minutes, but gradually this period increases to 7-8 hours. It is strongly not recommended to leave the seedlings of cabbage open at night, because in the spring frosts are possible.Ground preparation on site
To transplant cabbage to a permanent place, you will need a well-lit area with neutral soil acidity. If rooting cabbage seedlings on acidic soils, the plants will not die, but they will not give a good crop. Such an environment is favorable for the development of fungal and bacterial diseases, as well as keel, which neutralize fertilizers.
The increased acidity of the earth is indicated by:
- a whitish coating on the surface in the arable layer, resembling ash;
- accumulation of brown water in the holes with a rainbow film;
- horsetail, mint, plantain growing in the garden.
 Such events in the garden are relevant every 4–5 years. They are carried out in the fall, otherwise the risks of burning the root system of the vegetable crop are great.
Such events in the garden are relevant every 4–5 years. They are carried out in the fall, otherwise the risks of burning the root system of the vegetable crop are great.When planning a cabbage bed, you should pay attention to predecessors. The best are: potatoes, onions, garlic, carrots, legumes, cucumbers, beets, zucchini. It is not recommended to transplant seedlings to the place where cruciferous plants grew (radish, radish, rutabaga).Important! In the shade of bushes, trees and fences, cabbages will not be tied.
Valentine does not greatly deplete the soil, so it can be grown on the same site for 2 years in a row. But after that, a 3-year break is required.
In the autumn, on the selected site, the remains of the grown plants must be removed and mineral fertilizers applied before plowing. The nutrient mixture (per square meter) is prepared from:
The nutrient mixture (per square meter) is prepared from:
- double superphosphate (30–35 g);
- potassium sulfate (40-50 g).
Alternatively, you can use humus, compost or vermicompost (a bucket per square meter). But in this case, the amount of mineral fertilizing should be reduced by 2 times.
Transplanting seedlings into the ground
Around the second half of May, you can plan a transplant of cabbage to a permanent place. To do this, it is not necessary to wait for stable heat outside, as young plants can adapt to temperature conditions up to -3 ° C.
The transplantation process is preferably carried out in the evening or in cloudy weather. For this, the strongest and most healthy sprouts are selected. They are preliminarily watered abundantly with water at room temperature, and 3-4 hours after that, they are carefully transplanted together with an earthen lump into pre-prepared and moistened wells. If the crop was sown in peat pots, then they are simply placed in well-watered holes, the depth of which should correspond to the size of the seedling container.
If the crop was sown in peat pots, then they are simply placed in well-watered holes, the depth of which should correspond to the size of the seedling container.
Cabbage stalks should not interfere with each other, so they are placed 30–40 cm apart with 60–70 cm aisles. Experienced gardeners advise to leave several high-quality sprouts in case they need replacing unplanted specimens.
Did you know? The ancient Greeks believed in the miraculous properties of cabbage heads, using them to relieve intoxication. This plant has long been considered a symbol of sobriety.
Plant care
Variety Valentine quickly adapts to new conditions and in care is not much different from other hybrids. For a full-fledged vegetation, the plant needs moisture, nutrients, loose soil, enough light and moderate heat.
Features of watering
All cabbage loves water. Therefore, the bed on which the crop is cultivated should always be wet. In this case, a measure is important, because swampiness is fraught with the development of a pathogenic environment, and dry earthy coma can lead to the death of the root system.
To provide seedlings with comfortable conditions for growth, it is recommended to water the plantation after 2-3 days. Adult plants moisten once with an interval after 7 days. It is important to consider weather conditions. In hot weather, watering is recommended to be increased, and 2-3 weeks before harvesting, completely stop them. These measures will help protect the cabbage heads from cracking. If you have been absent from the garden for a long time and have not carried out regular humidifications, gradually bring the amount of water poured under the root of the water to the recommended norm.
It is important to consider weather conditions. In hot weather, watering is recommended to be increased, and 2-3 weeks before harvesting, completely stop them. These measures will help protect the cabbage heads from cracking. If you have been absent from the garden for a long time and have not carried out regular humidifications, gradually bring the amount of water poured under the root of the water to the recommended norm.
Modern gardeners resort to mechanical irrigation in the furrow, under the root, as well as sprinkling. However, the latter option contributes to the development of powdery mildew and rhizoctoniosis, since water enters the sinuses and poorly evaporates due to the density of foliage.
| Norms and frequency of cabbage irrigation | |
| The timing | Recommended Servings of Water |
| After transplanting seedlings | 8 liters per 1 m² or 1–1.5 liters for each bush with a frequency of 2-3 days |
| After adaptation of the stems and in the phase of active growth | 13 L on 1 m² |
| Head formation period | 20-30 liters per 1 m² |
| 2-3 weeks before harvest | — |
Important! Cabbage Valentine F1 can not be fermented immediately after harvesting. For pickling it must be kept in the cellar for at least 3 months for the disappearance of bitterness.
Fertilizer application
Given the late ripening of Valentine’s heads, this cabbage should be fertilized with potassium-phosphorus substances. They are responsible for forming quality heads that are suitable for long-term storage. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers will also not hinder, but in excess they can provoke cracking, as well as infection of the crop with rot and fungi. The proportions of the necessary fertilizing are calculated depending on the phase of development of the culture. The table below will help you with this.
The proportions of the necessary fertilizing are calculated depending on the phase of development of the culture. The table below will help you with this.
| Fertilizer rates for late ripe hybrids | ||
| When to deposit | Top dressing | Recommended rate for a single plant |
| 7 days after transplanting seedlings | A mixture of:
| 300-500 ml |
| 30 days after transplantation | A mixture of: • urea (10 g); • potassium monophosphate (10 g); • superphosphate (20 g); • water (10 l). | 1 liter |
| In mid-July, when heading begins | Mixture of: potassium sulfate (40–50 g); superphosphate (20 g); water (10 l). | 2-3 l |
If the plant is developing well, you can skip the first two nourishing procedures. They are mandatory in cases where the outlet is poorly leafy, and the sheet plates are small and underdeveloped. But in the period of tying the heads of dressing, skipping is undesirable. This work is best planned immediately after rain or after watering. At the final stage, the wells are sprinkled with fresh dry substrate or horse peat.
Important! In order for superphosphate to completely dissolve in water, it is necessary to prepare its extract. To do this, 20 tablespoons of the drug is poured 3 liters of boiling water and insist for a day, stirring occasionally. In the future, use the right amount of liquid fertilizer.
Loosening and weeding
Pure cabbage beds with soft, moist soil guarantee a high yield. After all, weeds not only deplete the soil, depriving the vegetable of nutrients, but also contribute to the development of colonies of pests and various diseases. In addition, when the moisture evaporates, the earthen hardens, impairing the oxygen supply to the roots, so experienced vegetable growers advise loosening the soil after each irrigation with a hoe. To the extent of growth of the stump, it is necessary to earthen the culture to the bottom foliage. Valentine is not mulched to avoid slugs in the garden.
Pests and diseases
The hybrid is characterized by increased resistance to a number of cabbage diseases, but with gross violations of the agrotechnical rules for growing a vegetable, the risks of its infection increase:
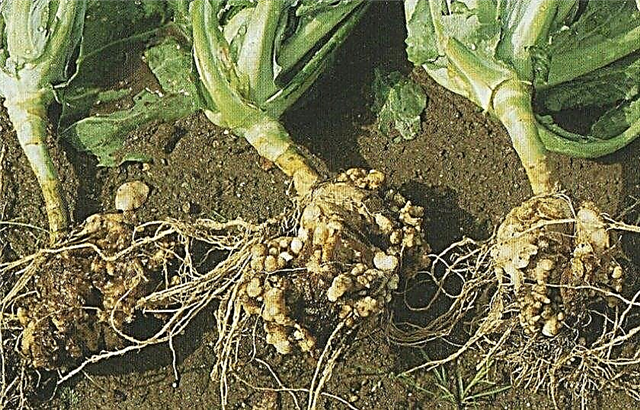
- Kiloy. This is a fungal infection whose pathogens are viable in damp. In the early stages of development, they penetrate into the cracks of the trunk and root processes. Over time, galls appear, the sizes of which increase with the growth of culture. As a result of infection, the supply of plant cells with nutrients and water is stopped, because of which the stalk fades, the formation of the head ceases. Treatment of the plant consists in adding river sand to the soil (a loose dry environment adversely affects fungi), as well as lime (required for alkalization). Irrigation with the participation of “Fundazole” (0.1% solution), colloidal sulfur (40 g per 10 l of water), “Cumulus” (40 g per 10 l of water) is also effective.

- Powdery Mildew The pedigree of the fungal infection can be neighboring cucumbers or berry crops. The disease is manifested by yellowing of the leaves on the inside and the appearance of a gray powdery coating. Dampness contributes to the development of spores. Treatment involves disinfection with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid. As an alternative, Ridomil Gold (25 g per 5 l of cold water) and Fitoftorin (7 g per 5 l of water) are suitable.

- Rhizoctonia. Infection with fungi occurs when transplanting seedlings due to increased soil moisture and water droplets that have fallen into the outlet. Young sprouts die due to drying of the root neck, and in adult plants, internal rotting is observed. To solve the problem, you will need to spray the Fitolavin culture (20 ml per 10 liters of water). Also, prophylactic treatment of seedlings in the stage of 2-3 leaflets will not be superfluous.

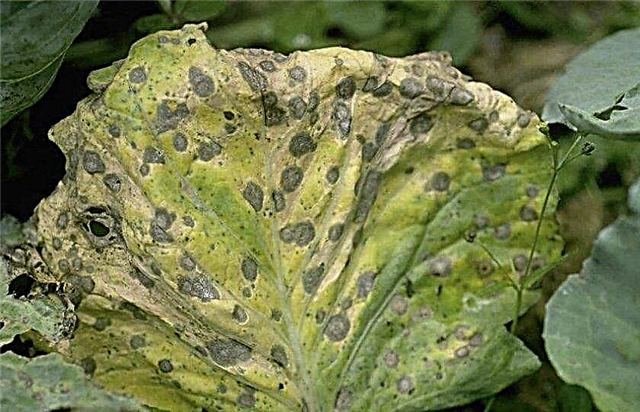
- Alternariosis (black spotting). The culture is vulnerable to pathogens in all phases of growth. In adult specimens, the foliage is covered with dark velvety dots up to 1 cm in size. If no measures are taken, leaves will die off, as a result of which the cabbage head will form loose. Dampness and temperature above + 22 ° C contribute to the development of fungal infection. Therapeutic measures include spraying with a 1% solution of Bordeaux fluid or copper chloride (45 g per bucket of water).

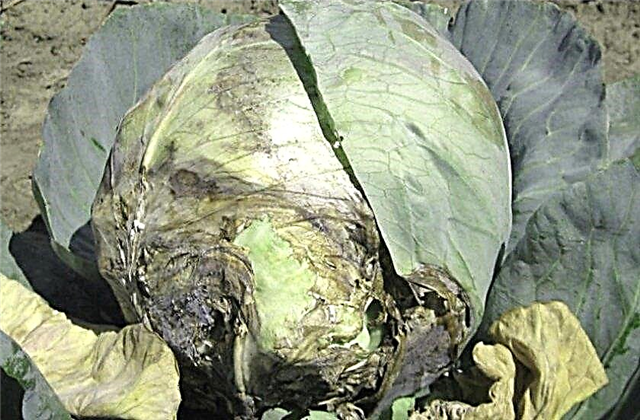
- Gray rot. The symptomatology of this fungal disease is more often manifested when the crop is harvested.Abundant irrigation or adverse weather factors contribute to its occurrence. Fungal spores penetrate damaged or frosty heads of cabbage, retain their viability in the cellar and can spoil all products. To solve the problem, thorough disinfection of the storage is necessary, as well as control of nitrogen-containing fertilizing of the culture.

In an unfavorable environment, Valentine can suffer from an invasion of pests:Important! Before consumption, it is recommended to thoroughly rinse the cabbage heads, and then dip them in salted cold water for half an hour. These manipulations will clean the vegetable from dirt and insecticide residues.
- cruciferous fleas;
- slugs;
- cabbage whites.
- marigolds that repel harmful insects;
- periodic watering of the beds with a solution of valerian (1 bottle is dissolved in 3 l of cold water);
- A ditch dug around the perimeter of the bed with wood ash, salt, mustard powder;
- deep autumn digging of the site;
- dusting a wet culture with shag or tobacco.
Harvesting and storage
The peculiarity of the Valentine variety is that holistic and not frosted heads of cabbage can be stored for up to 7-10 months. The hybrid is perfect for fresh consumption, since it retains its taste for a long time, and is also used for cooking various dishes involving heat treatment. Valentina can be fermented, but without pre-processing, the workpiece will be bitter. Fermentation is best prepared in the fall, cutting off substandard specimens that are unsuitable for long-term storage. For the winter, only integral elastic heads of cabbage are laid in the cellar. Harvesting involves digging up stitches along with the roots. After that, the remaining soil should be shaken off, cut the lower foliage, dried head out for 2-3 days and tied to a horizontal crossbar. In this form, cabbage will be much longer stored.
For the winter, only integral elastic heads of cabbage are laid in the cellar. Harvesting involves digging up stitches along with the roots. After that, the remaining soil should be shaken off, cut the lower foliage, dried head out for 2-3 days and tied to a horizontal crossbar. In this form, cabbage will be much longer stored.
Some housewives advise to wrap each head of cabbage in a cling film and put it separately on shelves. Ideal conditions for winter storage: cold -1 ... + 2 ° C and high humidity - 90–98%.
Cabbage Valentina deserves attention for its taste and marketability, as well as the stubbornness of the crop and the undemanding of its cultivation.