Recently, polycarbonate greenhouses have become widespread, in addition, ordinary greenhouses and hotbeds do not lose their relevance even today, a huge number of crops are grown in them. In the article we will talk about how to regulate the temperature in the greenhouse, as well as how to make a thermostat with your own hands and put it into practice.
What is thermoregulation in a greenhouse for?
In order to grow a high crop in a greenhouse, you must adhere to certain rules of cultivation and care, as well as ensure that the plants have a stable temperature and the absence of significant differences.
 When overheated, the plants will grow too fast and stretch, and too low a temperature will slow down their growth and disease.
When overheated, the plants will grow too fast and stretch, and too low a temperature will slow down their growth and disease.
Each plant needs a different temperature
It is the greenhouse that allows you to create the ideal mode for the life of plants, in contrast to their cultivation in open ground, since each plant requires a different temperature. The space of the room can be divided into zones in which the difference is several degrees. The optimum temperature is +20 ... + 22 ° C.
Temperature differences
Although the temperature control is carried out in the greenhouse, there is still a difference between the temperatures day and night. Differences occur due to the fact that there is no material in the greenhouse that accumulates heat. Permissible is the amplitude of the oscillations, not exceeding 4-8 ° C.
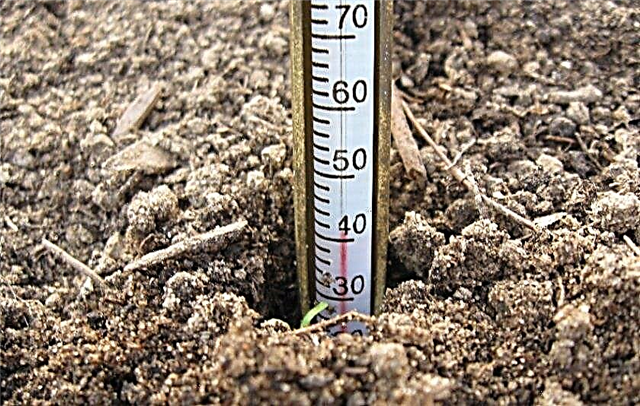
Soil temperature
The development of plants and their productivity depend not only on air temperature, but also on soil. At the optimum temperature of the soil layer, the root system of plants becomes powerful and assimilates nutrients well. If there is a drop in indicators by 10 ° C, phosphorus starvation begins in plants, they are depleted and die.

Greenhouse temperature controller options
The advantage of modern thermostats is the lack of need for constant independent manual adjustment of the temperature regime and the presence of a summer resident in the greenhouse. Modern technologies offer a choice of electronic, touch and mechanical controllers.
- All these types differ in design features and the principle of action:
- working to increase temperature indicators;
- working to reduce temperature indicators;
- combined.
Did you know? Polycarbonate is a very lightweight material. It is 16 times lighter than glass of the same size. All this reduces the pressure on the frame and makes the process of erecting a greenhouse simple and quick.
Electronic
These are modern devices with LCD screens, equipped with a thermistor, which serves as a sensor. They require a network connection and consume a small amount of energy. Electronic temperature controllers very accurately and quickly respond to temperature changes, due to which savings on heating are achieved.

One of their components is thermostats. They do not have moving components and assemblies, but there are semiconductor parts that allow accurate data to be provided.
To install such a device, follow these steps:
- Connect the remote sensor to the thermostat.
- Connect the fan to the thermostat.
- Set the desired temperature.
Important! The installation of such devices should be considered at the planning and assembly stage of the greenhouse.
Consider the electronic digital temperature controller TsTR-1, which is used in greenhouses. It is very accurate and sensitive, with an accuracy of ± 0.1 ° C and works in the range of adjustable temperature -40 ... + 125 ° C. Allowed maximum load 1.0 kW.
Since the temperature sensor does not have an airtight shell, it must be protected from water:
- Plug in the appliance. At the same time, 3 dashes (- - -) will appear on the indicator, after which the ambient temperature is displayed.
- To set the desired temperature, press the (-) or (+) button. When the indicator flashes, set the desired on and off value. After 5 seconds, the device will begin to work.
- Place the sensor where you want to adjust the temperature.
- Insert the plug of the heating device into the outlet on the device.
- The indicator readings gradually reach the desired temperature.
- After reaching the desired temperature indicator (on the indicator), monitor the readings throughout the day.

To control the electric soil heating system, the TR-50 is suitable. It has a sealed plastic case, is protected according to IP65 and is equipped with a remote sealed temperature sensor AS-10G with a cable length of 3 m.
Turn on and set the temperature, to block from accidental switching on, you can use one button on the front panel. You can set the temperature within +17 ... + 27 ° С. The device works with resistive heating and with a self-regulating cable.
Did you know? Electronic temperature controllers with air temperature sensors even work on battery power and can have a clock, calendar, and you can also look at the weather forecast on them.
Sensory
Such devices are among the most innovative. The advantage of sensory heat control is that it is possible to set different temperature indicators in different time periods, for example, night and day, as well as set the exact time of work. Another advantage is the mode of memorizing settings.

Sensor devices can control underfloor heating and heating cable. To mount the device, connect the terminals to the terminals according to the diagram on the back of the device or instructions: 2 contacts to the power supply - “zero” and “phase”, 2 - to the heating devices, and 2 - to temperature sensors.
Did you know? The record holder for the number of greenhouses is Holland. At the same time, the Dutch do not cover the structures with plastic, but with glass.
Mechanical
The mechanical temperature controller is characterized by the absolute independence of each individual device. It is an electrical installation equipment, the installation of which is carried out directly in the greenhouse itself. It belongs to the simplest and cheapest devices.
Suitable for correcting air temperature in small greenhouses, based on the temperature indicators of the soil. Electric "filling" is absent in them. There is a wide selection of various designs and components used on the market.

On the body of the membrane thermostat is a wheel with a scale. When you set the desired temperature using the device’s wheel, when it is reached, it will break or short-circuit the electrical circuit that feeds the heating device. In this case, the electrical appliance will turn on or off.
In the filling, as the main structural element, there is a gas membrane. The wheel connects to the membrane mechanism. When the wheel rotates, the membrane walls approach or move away from the control mechanism, as a result of which the temperature changes at which the circuit closes or opens.
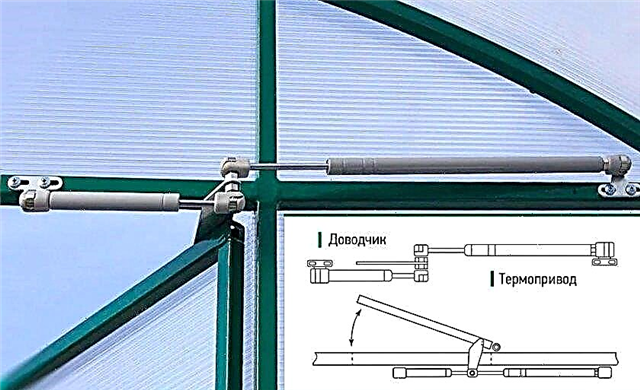
If the actuation mechanism is close to the membrane wall, the gas inside it must slightly change in volume in order for the device to work, accordingly, a lower temperature is needed, and vice versa. To connect the device, mount it in the wire that feeds the heater.
It has two terminals that can be connected to the heating system and at the same time to cooling. The main advantages of the device are its simplicity, reliability and efficiency compared to other types.
Important! When choosing a device, remember that maximum power matters. The connected load must not exceed it; otherwise, a contactor will be needed.
Do-it-yourself thermostat manufacturing
Since thermostats purchased may be too expensive, you can make them yourself. Widespread among gardeners received a device using a thermosiphon. Consider how to make it yourself and use it.
Tools
When making a thermosiphon, you may need a soldering iron, a hammer, pliers, a can for your cans, and a thermometer (to measure the temperature of the water).
Materials
You will need:
- 2 cans: one on 3 l and one on 1 l;
- copper tube with a diameter of 5-6 mm;
- 2 lids for cans: one metal (for preservation) and one of polyethylene;
- plastic hose.

How does it work
The principle of operation of the thermosiphon is quite simple:
- As the temperature in the greenhouse rises, water from a large can flows into a smaller one (it serves as a counterbalance), and a window (window) opens.
- With a decrease in temperature in a 3-liter can, a vacuum begins and water from a smaller capacity is sucked back. The weight of a liter can becomes smaller and the window closes.

Assembly and configuration
Follow these steps in sequence:
- Close a 3 liter jar with a metal lid.
- In the center of the lid, make a hole of suitable diameter to the copper pipe.
- Insert the tube into the hole in the cover.
- Solder the tube to the cap.
The operation of the thermosyphon must be checked.Important! This device does not require constant monitoring. From time to time, you only need to add water to a three-liter jar, the volume of which is reduced due to evaporation.
To do this, follow these steps:
- Pour 1000 ml of water into a large container.
- Put the jar in the bucket and pour water into it (it should not reach the lid of the jar).
- Fasten the hose to the copper tube and lower its other end into a smaller jar.
- Heat a bucket of water over a fire to + 25 ° C. The bank will create increased pressure and water from it will flow through a hose into a liter jar.
- Measure how much water has flowed out (optimally - 400 ml).

Now assemble the device:
- Hang a liter jar to the window.
- Pour 200 ml of water into it. At the same time, note that the weight of the can with the water poured into it should not open the window.
- Put a plastic lid on the jar, in which a hole is made and a hose is inserted (the end of the hose should not reach the bottom by 3-5 mm).
- When water from a large can begins to flow into a small one, the window should open.
Pros and Cons of a Homemade Regulator
- The advantages of a homemade regulator include:
- availability of materials for manufacturing;
- simplicity in manufacturing;
- quick assembly;
- universality.
- There are not many disadvantages of such a regulator, but they are:
- can only be used in summer greenhouses;
- requires observation and verification.
Thermostats will help to control and change the temperature regime in your greenhouse. When choosing the device that is right for you, consider the heating methods, the design of the greenhouse, the installation methods of the devices and their cost.












