Juniper Cossack (Latin name Juniperus sabina) - coniferous ornamental shrub, which belongs to the Cypress family. It is used in landscape design for decorating personal plots. A description of the varieties of the bush and simple tips will help to plant and grow a plant in your garden.
Description of Cossack Juniper
Juniper Sabina is an evergreen creeping shrub that is a representative of the genus Juniper. Sometimes a plant is a medium-sized tree whose height does not exceed 4 m. The trunk of such a plant has an arched shape and is covered with a reddish-brown bark, which has the property of exfoliating.

The dioecious bush reaches a height of 1–1.5 m. The natural environment for the growth of this species is the Caucasus Mountains, the Kabardinsky District, the rocky slopes of the Urals and Siberia, as well as forest tracts of steppe zones. The shoots of the plant are very poisonous and contain essential oil (3-5%).
Types of needles:
- in young specimens, the needles are needle-shaped, with pointed tips. Above is blue-green and soft. The length of the needles is 4-6 mm;
- adult plants have scaly soft needles, whose thick aroma is a characteristic feature of the variety.
Did you know? Within 24 hours, 1 ha of juniper spreads about 30 kg of phytoncides.
The needles remain unchanged for three years. The crown diameter is 2.5 m. Cossack juniper bears fruit with small rounded cones (volume 5–7 mm). Cones-berries are brownish-black, with a light bluish tint, two-seeded. The growth rate of the shrub is slow, annual growth is only 5 cm in height and 15 cm in width. Life expectancy of 50 years.
 Seed ripening occurs twice a year: in autumn and spring.
Seed ripening occurs twice a year: in autumn and spring.
Varieties
Description of varieties of Cossack juniper will help to choose the best option for landscape design. Shrub species has about 25 varieties.
Important! It is not recommended to plant Cossack juniper near the playgrounds, as the cones and needles of the plant are poisonous.
The most popular varieties:
- Tamaris (in Latin the variety is called Juniperus Sabina Tamariscifolia) Shrub height up to 1 m, crown diameter 2 m. Branches are short, grow vertically. The crown grows widely and eventually acquires a domed shape. Needle needles are slightly curved and painted in light green. The variety is common in the middle lane and in the north of Russia. Resistant to drought and low temperatures (withstands up to -35 ° C). The plant is unpretentious to the composition of the soil. It grows well on acid and alkaline land;
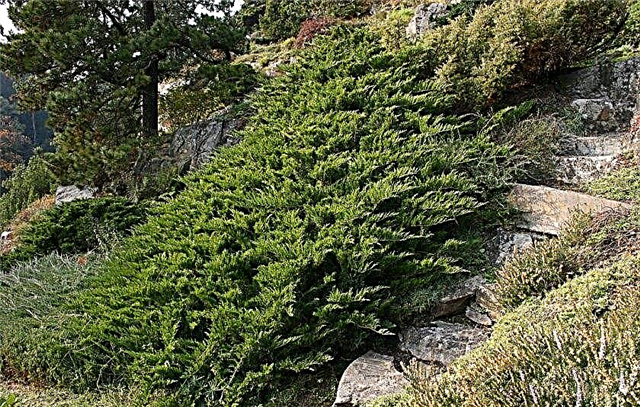

- Wegry. The height of the creeping shrub is 0.5 m, the volume of the crown is 2 m. The crown is large, spreading. Ascending shoots are covered with green needle needles. The variety is winter-hardy, drought-resistant. Suitable for growing on rocky terrain, as well as for landscaping slopes and ravines;

- There Nou Blythe (Juniperus sabina Tam No Blight) The height of the bush is 0.4-0.6 m, width 2 m. The shoots spread horizontally and grow in layers. The crown of an adult plant has a domed shape. The plant is slowly growing, in a year it adds only 10-15 cm. The needles are soft, dark green with a bluish tint. Coniferous aroma is pronounced. The bush is suitable for growing in rockeries and as a cover of rocky areas;
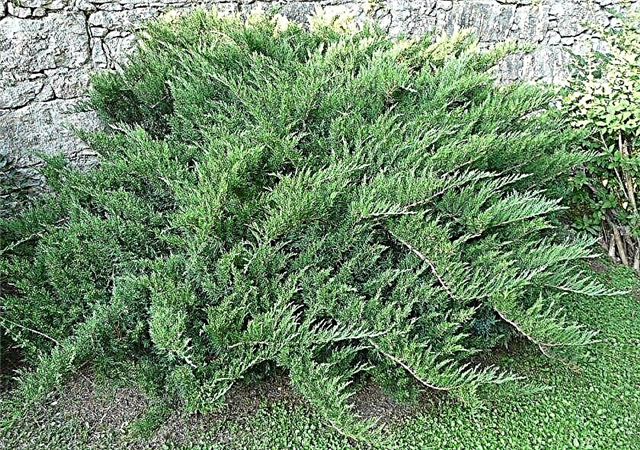

- Blue sparkle (Juniperus Sabina Blue Sparkle) The variety was bred in the 60s of the twentieth century. The height of the bush is 0.5–1 m, the diameter of the crown is 1.5 m. The crown is lush, grows widely. Branches grow vertically, the ends are up. The needles are scaly, needle-like with a slight bluish tint. The length of the needles is 4-6 mm. The smell is specific, coniferous, repels moths. It is used for landscaping park areas in combination with deciduous shrubs and trees. The variety is unpretentious in care, resistant to frost. All parts of the plant are poisonous;

- Hixie (Juniperus sabina hicksii) The adult bush reaches a height of 1.2 m, a width of 1.5 m. The shoots of a young plant grow vertically. They form a dome shape with age. Suitable for growing in urban environments for landscaping sidewalks and streets. The variety is quite resistant to low temperatures and is able to withstand up to -35 ° C;
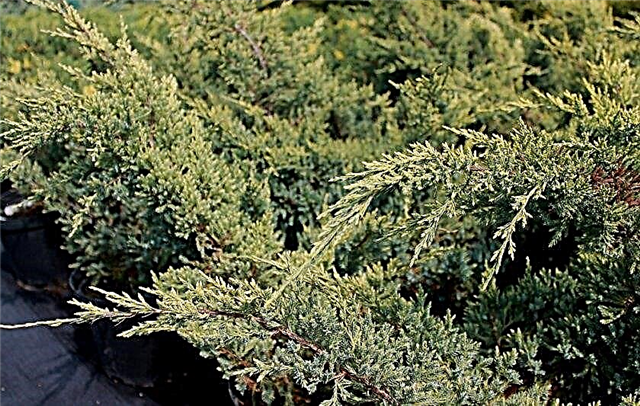

- Broadmoor or Broadmoor (Juniperus sabina broadmoor) Outwardly, the shrub resembles the Tamaris variety. The height is approximately 0.5 m. The width of the crown reaches 3.5 m. Durable and delicate shoots are covered with short needle needles of gray-green color, arranged horizontally;

- Erect (Juniper Sabina Erecta) Ornamental shrub about 2 m high. The ascending branches form a pyramidal crown. Dark green needles have a scaly structure. The variety is compact and suitable for group plantings;
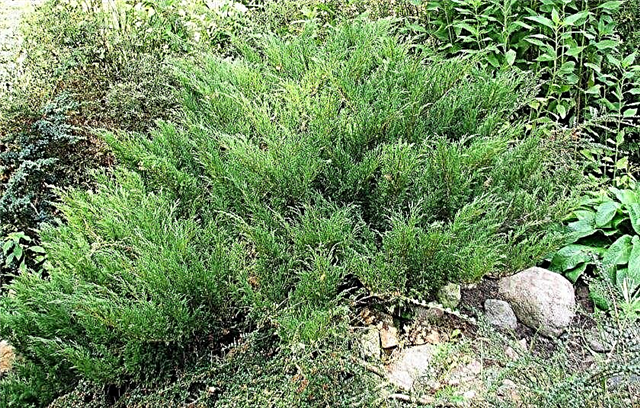

- False Cossack (Juniperus Pseudosabina) A variety of juniper ordinary, which is found in Western and Eastern Siberia. The species is slow-growing, resistant to high and low temperatures (up to -35 ° C). Needle needles. The needles are not sharp, the length is 3 mm. Creeping branches. Planted as a cover of rocky areas.
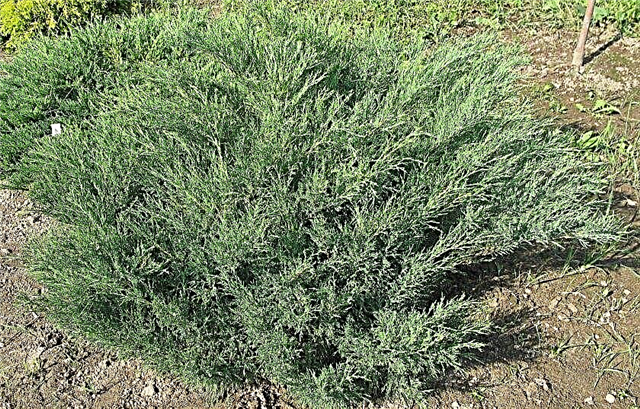

Landscape design application
In landscape design, Cossack juniper is used for landscaping parks and city streets. To decorate personal plots, it is planted singly or in group plantings. With deciduous plants forms a harmonious composition.
Squat shrubs look great under tall trees. Thanks to the creeping branches, the juniper groups form dense thickets that cover the stony areas and slopes with a dense cover.
Growing plants
Juniper cultivation begins with planting. However, you need to properly prepare for planting, so that in future the plant grows well and does not cause additional trouble.
Stages of preparation:
- seat selection;
- soil preparation;
- selection of planting material;
- landing.
How to plant Cossack juniper
First of all, you need to decide on the place where the young bush will grow. Juniper is a photophilous plant, so it requires the most open space with good lighting.
 In addition, it should be borne in mind that the branches of the shrub grow very much and for full development, as well as preserving the natural shape of the crown, it needs to provide enough free space.
In addition, it should be borne in mind that the branches of the shrub grow very much and for full development, as well as preserving the natural shape of the crown, it needs to provide enough free space.
Soil preparation involves the preparation of a soil mixture. It is prepared from peat, turf land and sand in a ratio of 2: 1: 1. It is recommended to lime the prepared mixture with dolomite flour or ground limestone in the calculation of 80–100 g of substance per volume of one pit. The average pit size is 50 cm in depth and 60 cm in width.
As a planting material, you need to choose healthy seedlings. The root system should not have signs of disease or pest damage (dry and rotten roots). The seedlings that are in the container must be abundantly watered and the roots absorb moisture.
If the planting material was purchased with an open root system, it must be temporarily placed in a bucket of water for several hours, then treat the roots with a stimulant, for example, “Kornevin”. After completing the preparation, you can begin to plant.
Important! In group plantings, shrubs must be planted at a distance of 0.5 m from each other.
Landing pattern:
- Dig a pit 50 × 60 cm.
- At the bottom of the pit lay out a drainage layer of 20 cm. As a drainage material, you can use crushed stone, broken pieces of brick or stones.
- Pour out the prepared soil mixture (peat, turf land, sand).
- Plant a seedling in a pit so that its root neck rises 10 cm above the ground.
- Fill the foundation pit with the remaining soil mixture and tamp.
- Pour 12 liters of water. When the earth completely absorbs moisture, fill the trunk near the trunk with pieces of pine bark and a peat layer of about 5 cm.

Juniper Care
After planting, the young plant must be provided with conditions suitable for development and growth. To grow a healthy and beautiful bush, you need to learn how to properly care for it.
Care Features:
- pruning
- watering;
- top dressing.
Next, you should understand the intricacies of these procedures.
Pruning
In spring or autumn, it is necessary to carry out sanitary pruning of the plant. To do this, remove all dry and diseased shoots. To give a decorative form, the bush also needs to be trimmed. It is important to consider that juniper is a slowly growing shrub, therefore only the ends of the branches should be cut, about 2 cm.
The procedure should only be done with gloves, since the shoots of Cossack juniper contain toxic sabinol oil. If this substance gets on the skin, itching and burning are observed for a long time.
Video: topiary haircut of Cossack juniper in nivaki style
Watering
The plant is unpretentious in care and does not require frequent watering. Moisten the bush only in the hot season. The frequency of watering in the summer is only 2-3 times a season. One shrub accounts for about 30 liters of water. After moistening, the soil needs to be slightly loosened and weeds weeded. It is also recommended to irrigate the crown in the morning and evening. Sprinkling additionally moisturizes the air and allows you to wash off the dust from the top of the plant.
Fertilizer application
It is necessary to feed the bush in the spring, in April or May. You can fertilize with Nitroammofoskoy at the rate of 30 g of funds per m². Also, Kemira Suite is a good fertilizer. This top dressing needs to be planted in water: 20 g per 10 L. Well-chosen and applied fertilizers have a positive effect on the growth of shoots and the quality of needles.
Did you know? Based on different parts of juniper, tinctures and decoctions are prepared for the treatment of skin diseases. The pharmaceutical industry also uses this plant for the production of anti-inflammatory drugs.
How to propagate juniper Cossack
Material for planting can be purchased at the store or try to propagate the plant yourself at home.
Reproduction methods:
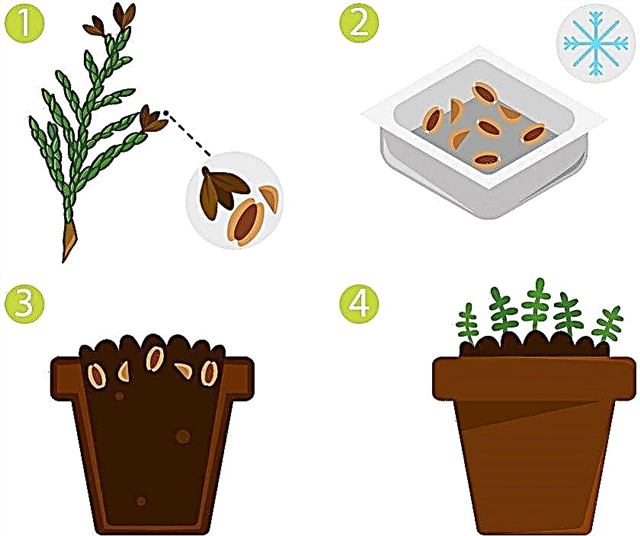
- Seeds. In autumn, you need to collect the cones and carefully extract the seeds from them. Then soak in a solution of sulfuric acid for 10 minutes. After this time, rinse with plenty of water. Further, the seeds must be stratified by sowing them in the snow for 5 months. In the spring, when young shoots appear, transplant into open ground.
- Cuttings. In spring, preferably in cloudy weather, you need to prepare cuttings. To do this, you need woody branches growing at the top of the bush. Selected shoots should not grow vertically, it is desirable that they are drooping. Cutting the stalk, you need to make sure that there is a “heel” on it - a fragment of the shoot or branch. Then you need to remove 5 cm of needles, without touching the "heel". Next, you should immediately plant the cuttings in a substrate of peat and river sand in equal parts. It is necessary to deepen by 3 cm, observing an angle of 60 °. Then planting should be poured with sodium humate or “Heteroauxin” - a drug that stimulates root growth. Store cuttings in greenhouse conditions with high humidity, at least 90%. In this case, the temperature regime must be observed within +17 ... + 19 ° С. After budding, increase the temperature to + 25 ° C. The process of root formation takes from 50 to 90 days. You can plant young plants in the open ground next spring. During the rooting period, cuttings need to be watered 5 times a day. After the first roots and buds open, reduce watering to once a week.

- Layering. It is possible to propagate a bush by this method throughout the entire growing season. To do this, choose green, but developed and mature shoots. Then prepare the soil: loosen the soil, fertilize with acid peat and river sand, water. Next, from the base of the selected branch, you need to remove 20 cm of needles and, bending to the ground, fix. In this case, the top should be above the surface. The soil around the attached branch must be loosened periodically. Layers take root throughout the year. After root formation, seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place.

- Vaccinated. The grafting method is used to propagate valuable varietal forms. For this purpose, a stalk cut from a certain variety is grafted to an ordinary juniper seedling. To do this, push the handle against the stock and tightly fasten with tape.
Benefit and harm
Before proceeding with the cultivation of juniper Cossack, you need to familiarize yourself with its beneficial and harmful properties. For example, to understand why rust attacks an apple tree or a pear, you need to pay attention to the proximity of plants.

If juniper grows nearby, then most likely it is the source of the spread of the fungus Gymnosporangium sabinae, which is the causative agent of this disease. Spores of the fungus spend the winter in the cones of the bush, and in the spring they spread throughout the garden.
- Positive traits:
- Decorativeness;
- Needles are suitable as mulch and fertilizer for flowers;
- Shoots contain volatile, having an antibacterial effect;
- Juniper aroma repels parasites and pests.
- Negative qualities:
- In winter, the plant changes needles and looks untidy;
- Fallen needles decay within 3-5 years, so the fertilizer will not be ready soon;
- All parts of the plant are poisonous;
- The substances contained in the shoots, needles and berries are toxic and affect the central nervous system, digestive organs and kidneys.
"Cossack" juniper is planted to decorate the landscape. Growing this unpretentious plant is relatively simple. When deciding to plant a decorative shrub in your garden, it is important to remember that it has both beneficial and harmful properties.