Not many indoor plants have such a bright yellow color as allamanda. Despite the difficult care, it attracts many gardeners. And that's why.
Flower description
In nature, allamanda grows in tropical forests in the form of evergreen vines, shrubs or trees. Representative of the Kutrov family. Cultivated are only some bush specimens and creepers. A plant with light, green, egg-like leaves, growing in whorls of 3-4 pieces. Pleases large (with a diameter of about 8-10 cm), mainly yellow flowers, all summer. The flowers are tubular, funnel-shaped.
In indoor cultivation, the allamanda laxative is most often found.
Less common are the following types of allamanda:
Pros and Cons of a Houseplant
- This exotic plant is grown, because the benefits are significant:
- very beautifully braids all kinds of supports;
- has large, very spectacular flowers;
- growing fast.
Did you know? All parts of the plant are poisonous, but the allamanda laxative is used in folk medicine to make preparations to increase the motility of all parts of the intestine.
- Allamanda also has enough disadvantages:
- this tropical plant is capricious in relation to the conditions of detention, therefore it is more suitable for greenhouses;
- Indoor rarely blooms;
- takes up a lot of space, needs support and regular pruning.
But even the disadvantages of this exotism do not scare gardeners, and many still breed it at home.
Growing allamanda at home
Before purchasing this flower, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with the features of cultivation and care.
Conditions and location choice
When choosing a plant location, you need to consider the following points:
- very fond of warmth and sunlight. Able to tolerate even exposure to sunlight, but in a limited amount. When the sun is too scorching, the plant is shaded. Suitable place - windows located on the south side;
- poorly reacts to drafts, dry air, and therefore, to the neighborhood with appliances for heating;
- grows quickly and has a fairly overall dimensions.
For good growth, allamanda needs to provide the following conditions:
- in summer, the comfortable temperature will be from +20 ° С to +22 ° С, and in winter - from +15 ° С to +18 ° С;
- humidity should be maintained at 60–70%. To achieve this result, it is possible to carry out spraying (1-2 times a day) with warm, settled water. When spraying, moisture is not allowed on the flowers. A container of water can be placed next to the pot (this will also help increase the moisture content in the air);
- the soil should be sufficiently moistened, but the top ball should dry before the next watering. You can maintain the moisture of an earthen coma by placing the pot on wet peat or sand. It is necessary to ensure that drainage does not provoke decay of the roots.
Did you know? In cold and rainy weather, the flowers of allamanda become darker.
Watering and feeding
Allamanda is a very moisture-loving flower, therefore it requires frequent watering, especially in the summer. But the earth should not be too wet. In winter, the amount of watering is reduced. The soil must not dry out. As soon as the top ball dries, you need to water it.
For top dressing, universal complex fertilizers for flowering plants are used (for example, Aquarin or Watering Can). They are introduced 1-2 times a month in the spring-summer period. At rest (from late autumn to spring), the plant is not fed.
Transfer
It is necessary to transplant the plant as the rhizome grows. Fast-growing (mostly young) specimens are transferred to new containers almost every year. Adult individuals are transplanted when the roots completely fill the pot, that is, every 2-3 years. Do it in the spring.
In order not to injure the flower, it is transferred to a new container (2-3 cm larger in diameter from the previous one) together with an earthen lump. The empty space is covered with a loose fertile substrate.Important! Young allamanda can be transplanted twice a summer.
You can buy a ready-made soil mixture or prepare it yourself:
- 1 part of turf and humus;
- 2 parts of leaf land and peat;
- 0.5 parts of sand.
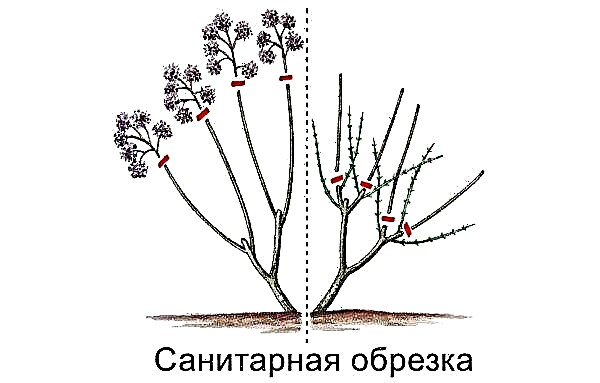
Pruning
This plant is fast-growing, therefore, for a compact and beautiful appearance, it needs to be cut. When trimming, slices are made only over leaf nodes.

Among the cropping methods used are:
- regular pinching of the top of the shoots is the best way to maintain decorativeness;
- annual pruning, which is carried out in the last days of November, before the plant enters the dormant stage. It consists in shortening all branches by 1/2 or 1/3 of the entire length;
- constant sanitary pruning (involves the removal of thin, weakened and too thick branches).
If you want to get not a bush, but an ampelous plant, then autumn pruning is not necessary. Growing shoots should be tied to established supports.
Propagation Features
Allamanda can be propagated by cuttings or seeds.
Cuttings
Rooting cuttings consists of several stages:
- Cut processes 8-10 cm each.
- Cut the slice with Zircon and deepen into the soil mixture (1 part peat and sand).
- Pour and cover with a film or plastic bottle to create greenhouse conditions.
- During the rooting period (2-3 weeks), the temperature is maintained at about + 24 ° C. Airing and spraying with warm water are carried out.
- Cuttings with emerging roots dive into a new substrate (1 part of turf, humus and sand).
- In the future, care is the same as for adult plants.

Seeds
This method is longer, since seedlings appear after 30-40 days.
The order of your actions is as follows:
- Soak the seed material for 1-2 days in water.
- Treat with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.
- Sow to a depth of 2 cm in a mixture of peat and sand (1: 1). Cover with a film.
- Ventilate daily. Water as needed. Temperature - not lower than + 25 ° C.
- Remove the film after emergence and move them to a well-lit place.
- When the sprouts reach a height of about 7 cm, they are dived into separate containers with soil for adult specimens.
Growing difficulties
When growing allamands, you may encounter such problems:
- from severe waterlogging of the substrate rotting of the roots and base of the stem may begin. To prevent this, do not abuse watering;
- yellowness of leaves, poor growth and poor flowering (or lack thereof) may be caused by a lack of light and nutrients. It is necessary to rearrange the flower to a brighter place and fertilize with the complex dressings indicated in the section “Watering and dressing”.
- twisting and browning of leaves cause drafts, cold, and also an excess of moisture in the soil. It is necessary to raise the temperature to the desired level and reduce watering.

The plant can be affected by sucking (aphids and whiteflies) and gnawing (nematodes and ticks) pests:
- aphids are removed with soapy water (1 part soap and 6 water), into which a sponge dips, with which the affected leaves are treated;
- the whitefly is removed by wiping the leaves with a cotton pad dipped in alcohol. After treatment, in order to avoid burns, the plant is washed under a warm shower;
- in the fight against spider mitesthat bite into leaves and stems, prevention is important. The pest loves dry air, so you need to spray more often. When ticks appear, the plant is treated with ultraviolet light. The lamp is placed so that the lower part of the leaf plate is illuminated, where the pest is located. In severe cases, the flower is processed by Fitoverm;
- fight the nematode (hitting the roots) is practically useless. It’s easier to destroy a flower. But you can try the biological product "Nematofagin." Use it according to the instructions.
Important! When working with allamanda, you should remember that it is poisonous, so you need to wear gloves and keep away from children and pets.
The article highlights the most important points in the cultivation of allamanda. By correctly applying information on the cultivation of this exot, the plant will bloom for a long time.